In today’s fast-paced digital world, efficient communication remains at the core of every successful business. Whether it’s a small startup or a large enterprise, reliable voice communication systems can streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer service. Among the many devices that play a role in this space, the FXO Gateway stands out as a key component for integrating traditional telephony systems with modern VoIP technology.
But what exactly is an FXO Gateway? How does it work? And why should businesses care?
In this blog, we’ll explore the definition, functionality, benefits, and use cases of FXO Gateways, helping you understand why they are essential in hybrid telecommunication infrastructures.
Explore More of Our Products Here:
What is an FXO Gateway?
An FXO Gateway (Foreign Exchange Office Gateway) is a device that connects analog telephone lines (PSTN) to a VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) network. It essentially allows legacy phone systems and analog lines to communicate with digital IP-based systems.
In simpler terms, an FXO Gateway acts as a translator between old-school telephone lines and modern IP-based communication platforms. This is particularly useful for organizations transitioning from traditional telephony to VoIP but still want to utilize existing analog infrastructure.
FXO vs. FXS: Understanding the Basics
Before diving into how an FXO Gateway works, it’s important to understand the difference between FXO and FXS:
- FXO (Foreign Exchange Office): This interface connects to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). Devices with FXO ports receive analog line signals.
- FXS (Foreign Exchange Station): This interface delivers analog line signals to end devices like telephones or fax machines.
In this context, the FXO Gateway connects to the FXS port of a PBX system or PSTN line, allowing analog telephone signals to be routed over a VoIP network.
How Does an FXO Gateway Work?
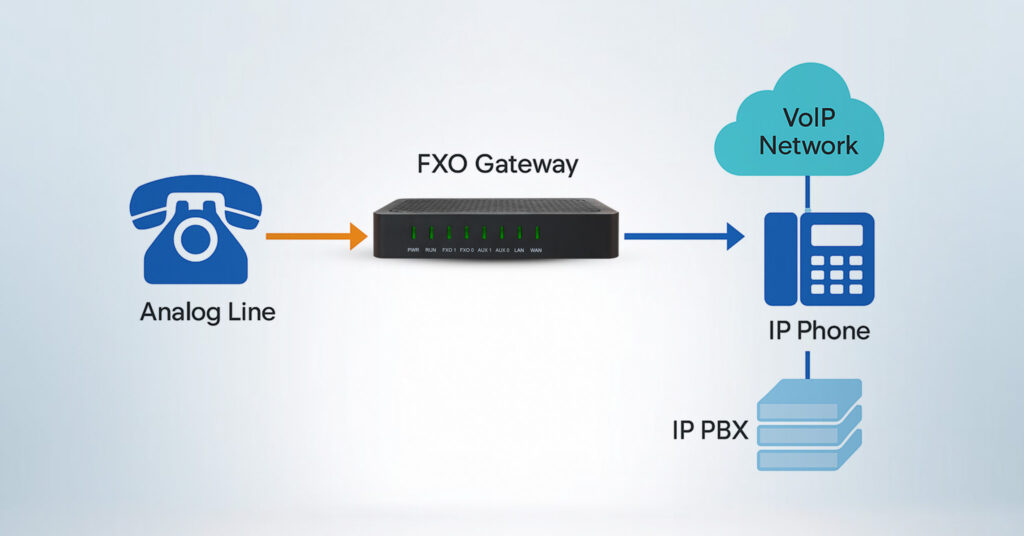
An FXO Gateway functions as a bridge between traditional phone lines and IP-based networks. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
1. Analog Line Connection
The gateway connects to one or more PSTN analog phone lines using its FXO ports. Each port corresponds to a single phone line.
2. Signal Conversion
When a call comes in from the PSTN, the FXO Gateway converts the analog signal into digital packets using a codec (such as G.711 or G.729). This makes it compatible with SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) or other VoIP protocols.
3. SIP Communication
The gateway communicates with the IP PBX or VoIP server using SIP, enabling the analog call to be routed through the IP network to the correct IP endpoint.
4. Call Termination
If an outgoing call is made from an IP-based device to a traditional phone number, the FXO Gateway performs the reverse process: converting digital VoIP signals back into analog to route the call over the PSTN.
Explore More of Our Products Here:
Key Features of an FXO Gateway
Modern FXO Gateways come packed with powerful features, including:
- Multiple FXO Ports: Typically ranging from 2 to 32 ports, supporting various analog lines.
- SIP Protocol Support: Enables seamless communication with VoIP systems.
- Codec Support: Includes G.711, G.729, G.723.1 for efficient bandwidth usage.
- Echo Cancellation: Enhances audio quality by reducing echo.
- Caller ID Support: Identifies the calling party even from analog lines.
- Failover Mechanism: Ensures continued operation in case of IP network failure.
Why Use an FXO Gateway?
FXO Gateways play a crucial role in hybrid communication environments. Here’s why they matter:
1. Leverage Existing Infrastructure
For businesses with existing analog phone lines or legacy PBX systems, FXO Gateways provide a cost-effective way to integrate with VoIP without a complete overhaul.
2. Lower Communication Costs
By routing calls through VoIP networks where possible, businesses can significantly reduce long-distance and international call charges.
3. Reliable PSTN Backup
Even in a VoIP environment, having a connection to the PSTN via an FXO Gateway ensures communication continuity during network failures.
4. Local Call Termination
FXO Gateways enable local call termination from remote locations, which can be crucial for companies with distributed teams or regional branches.
5. Flexible Deployment
FXO Gateways can be deployed in various topologies — at headquarters, branch offices, or remote sites — depending on the network architecture.
Popular Use Cases of FXO Gateways
1. Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs)
Many SMBs operate with limited budgets and existing analog infrastructure. FXO Gateways allow them to adopt VoIP gradually while retaining PSTN access.
2. Call Centers
Call centers often receive high volumes of calls from traditional lines. FXO Gateways help route these calls efficiently to IP-based agents.
3. Hotels and Hospitals
Organizations with hundreds of analog extensions can use FXO Gateways to integrate these lines with modern VoIP systems.
4. Remote Office Connectivity
FXO Gateways can connect remote or rural office locations with the central VoIP network, even where digital connectivity is limited.
Explore More of Our Products Here:
Choosing the Right FXO Gateway
Selecting the best FXO Gateway depends on several key factors:
1. Port Density
Port density refers to the number of FXO ports available on the gateway, which determines how many analog phone lines you can connect. If you have only a few analog lines, a 2 Port or 4 Port FXO Gateway might be sufficient. However, larger businesses or organizations with multiple lines will require gateways with higher port counts, such as 16 Port or 32 Port FXO Gateways. Choosing the right port density helps optimize costs and scalability—too few ports can limit your capacity, while too many can increase unnecessary expenses.
2. Compatibility
Compatibility is critical to ensure the FXO Gateway integrates smoothly with your current telephony system. Most modern gateways support SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), the standard protocol for VoIP communications. You need to confirm that the gateway supports the specific SIP version and signaling methods your IP PBX or VoIP provider requires. Compatibility also includes ensuring the gateway supports your network’s codecs, security protocols (like TLS or SRTP), and any special features your system uses.
3. Call Volume
The call volume is the number of simultaneous calls your system handles regularly. If your organization expects high concurrent calls, you must select an FXO Gateway that can efficiently manage that load without dropping calls or reducing quality. Devices vary in their processing power and capacity to handle call sessions. Overloading a gateway can cause performance issues, so estimating call volume helps pick a device that meets demand now and in the future.
4. Voice Quality
Voice quality is a crucial factor affecting communication clarity and user experience. Look for FXO Gateways that support advanced audio codecs like G.711, G.729, or Opus, which balance bandwidth use and sound quality. Additionally, features such as echo cancellation remove audio feedback, and jitter buffering smooths out variations in packet arrival times, preventing choppy or distorted sound. These technologies ensure calls are clear, natural, and free from technical issues.
5. Management and Monitoring
Ease of management impacts how efficiently your IT or telecom staff can configure and maintain the gateway. Devices with a user-friendly web-based interface allow remote configuration, troubleshooting, and firmware upgrades without physical access. Some gateways also support SNMP monitoring for integration with network management systems, providing real-time alerts and performance statistics. Efficient management reduces downtime and simplifies ongoing maintenance.
6. Brand Reputation
Choosing a well-known and trusted brand ensures you receive a reliable product backed by strong customer support and regular firmware updates. Brands like Dinstar, Grandstream, and Cisco have established reputations for quality and durability in the telecom industry. They offer ongoing software patches to address security vulnerabilities and add new features, plus professional support if issues arise. Investing in a reputable brand minimizes risks and ensures long-term stability.
Conclusion
An FXO Gateway is an essential device for businesses looking to blend traditional analog telephony with modern VoIP networks. Whether you’re upgrading to an IP-based system or maintaining hybrid communications, FXO Gateways offer flexibility, cost-efficiency, and reliability.
By understanding what an FXO Gateway is and how it works, you’re better positioned to make informed decisions that support your organization’s communication strategy.



